
Further analysis excluded false negatives and signals from the nearby target HD 13908.
#Iridium communications inc software#
Our analysis, utilizing the turboSETI software developed by BL, did not detect any signal indicative of a non-human-made artificial origin. We searched for radio signals directed at the inner solar system from such a source in the L and S bands. As a first target, we searched for a relay at the focus of the Alpha Centauri AB system while correcting for the parallax due to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Here, we demonstrate a search across a wide bandwidth for interstellar communication relays beyond the Sun’s innermost gravitational focus at 550 au using the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) and Breakthrough Listen (BL) backend. If there are probes within the solar system connected to such a network, we might detect them by intercepting transmissions from relays at these foci. If the Sun is part of such a network, there should be probes at the gravitational foci of nearby stars. Stars provide an enormous gain for interstellar communications at their gravitational focus, perhaps as part of an interstellar network. Finally, a compilation of current research activities and potential research topics is proposed, identifying problems and open challenges that can be useful for researchers in the field. The survey also provides a discussion on emerging data-driven synchronization techniques based on Machine Learning (ML). This article also provides an extensive list of applications and examples of synchronization techniques for DSSs in addition to the most significant advances in other operations closely related to synchronization, such as inter-satellite ranging and relative position. Then, the synchronization methods reported in the literature are reviewed and categorized. First, some important architecture and system concepts are defined. In this context, this survey aims to summarize and categorize the most relevant results on synchronization techniques for Distributed Satellite Systems (DSSs). Thus, the development of precise, robust, and resource-efficient synchronization techniques is essential for the advancement of future CDSSs. In addition, satellite systems have significant resource constraints, especially for small satellites, which are envisioned to be part of the future CDSSs. When clock or local oscillator signals are generated locally at each of the distributed nodes, achieving exact synchronization in absolute phase, frequency, and time is a complex problem. However, they have to meet strict synchronization requirements before their use is generalized. Use L-band frequencies, with Frequency Division Multiple Access and Timeĭivision Multiple Access (FDMA/TDMA) multiplexing to make the mostĬohesive Distributed Satellite Systems (CDSSs) is a key enabling technology for the future of remote sensing and communication missions. There will be no bypass of sovereign territory due to the Parties of each telephone call, including the country of origin or The global communications network will provide revenue to all This activity provides globalĬommunication even if the subscriber's location is unknown to theĬaller. Telephone call, initiate connections, and terminate the telephone call Through a network of ground gateways, establish the path of the

Will track the location of the telephone handset, determine routings
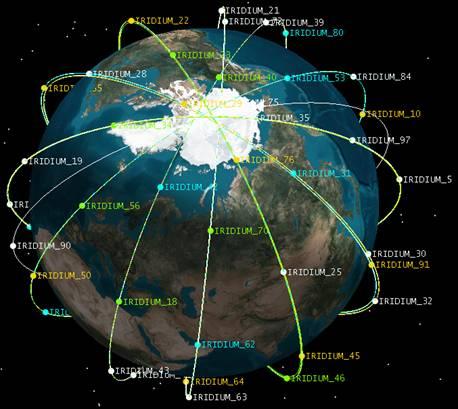
The 66 satellite interlinked constellation system Services-voice data, fax, paging-to connect to destinations virtuallyĪnywhere on earth. The IRIDIUM system is a satellite-based, wireless personalĬommunications network designed to permit a wide range of telephone


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
